Jumper (J)
A jumper is a conducting wire used to connect two contacts without creating a significant resistance. They are mostly used to modify circuit behavior by changing the electrical path.
Switch (S)
A switch allows the user to either close or interrupt the circuit by a mechanical action.
Relay (K)
A relay is an electromagnetic switch that closes / opens the load circuit when current flows / not flows in the control circuit.
Fuse (F)
A fuse consists of a fusible element. This element melts when the current passing through it heats it excessively due to prolonged high current. Once the element melts, the circuit is interrupted.
Resistor (R)
A resistor absorbs a portion of the voltage and reduces the current in the circuit. This allows other components in the circuit to be supplied with the appropriate voltage and current.
- Potentiometer: Mechanically adjustable resistor
Capacitor (C)
A capacitor is a storage device based on an electric field. When a circuit is established, it charges. Once the circuit is interrupted, it discharges, generating current.
Diagram ▼
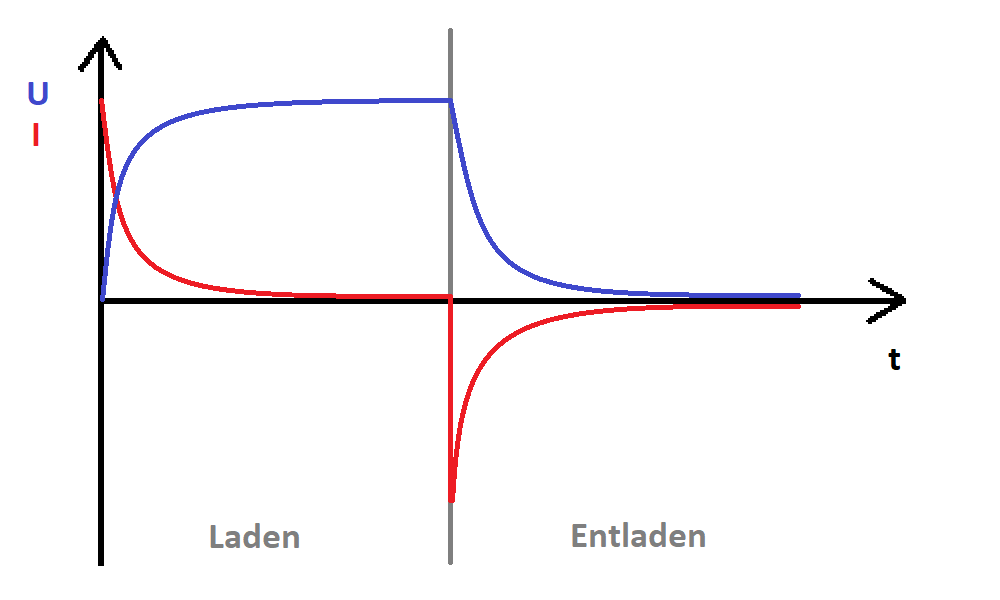
In an alternating current circuit, it acts as a resistance (capacitive reactance).
Inductor (L)
An inductor is a storage device based on a magnetic field. When a circuit is established, it charges. Once the circuit is interrupted, it discharges, generating current.
Diagram ▼
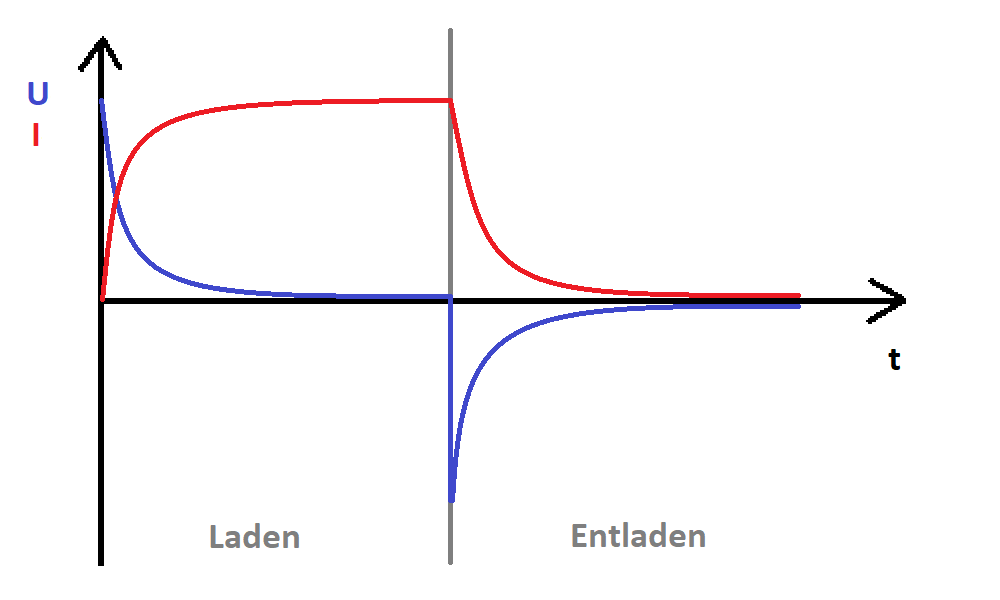
In an alternating current circuit, it acts as a resistance (inductive reactance).
Transformer (T)
A transformer changes voltage and current of an alternating current from the input to the output depending on the different number of turns of the two respective coils.
Diode (D)
A rectifier diode allows current flow in only one direction. In the forward direction, it requires a minimum voltage for current flow, and in the reverse direction, there is a maximum voltage above which it is destroyed.
- Zener diode: Operates in reverse direction for voltage stabilization.
- Light-emitting diode: Operates in forward direction for light emission.
Transistor (Q)
A transistor acts as both an electrical switch and an amplifier. If a voltage equal to or above the threshold voltage is applied between the base and emitter, an amplified current flows from the collector to the emitter.
Integrated Circuit (IC)
An integrated circuit is a component that combines many interconnected components (transistors, diodes, etc.) on a chip. Many contacts (pins) are often available to control this chip.
- CPU: A very complex integrated circuit.
